Key takeaways
- The post defines “man-made” fruits and vegetables as foods shaped over time through selective breeding and cross-breeding, not direct DNA modification.
- It contrasts this with GMOs and explains why selective breeding has been used (yield, flavor, and disease resistance).
- The article also discusses the sustainability claims it makes about breeding for crops that need fewer inputs and reduce waste.
- It lists examples it calls man-made, including broccoli, apples, bananas, cauliflower, corn, strawberries, eggplant, tomatoes, and watermelon.
Fruits and vegetables are crucial parts of a nutritious, balanced diet, should include a variety of fruits and vegetables, and most of all in sufficient amounts of each. Vegetables and fruits that are man made have their roots in early agricultural practices when people started selecting breeding plants to create desired traits like higher yields, better flavor, and disease resistance. This technique has throughout time, produced diverse fruit and vegetable types with distinctive tastes, textures, and colors.
In order to generate offspring with desired features, selective breeding, a common technique for producing manufactured fruits and vegetables, entails crossing plants having those traits.
What are man made fruits and vegetables?
Man made fruits and vegetables are plants carefully grown or altered to achieve particular qualities. Over time, these fruits and vegetables undergo various modifications, such as cross-breeding or hybridization. This process began as a result of the quest for increasingly eco-friendly farming techniques, the imperative to feed a fast-expanding global populace, the drive to decrease food waste, and increase crop yields. Man made fruits and vegetables, as opposed to GMOs (genetically modified organisms), rely on natural genetic variety rather than direct alteration of an organism's DNA.
Producing man made fruits and vegetables lowers the use of chemicals and other artificial interventions. By requiring less chemical input and increasing crop yields, these products can contribute to more sustainable agriculture. Furthermore, they ensure the effective production of food with less negative environmental impact.
What fruits are man made, and which vegetables are man made? Here is a list of man made fruits and vegetables you should know.
What vegetables and fruits are man made?
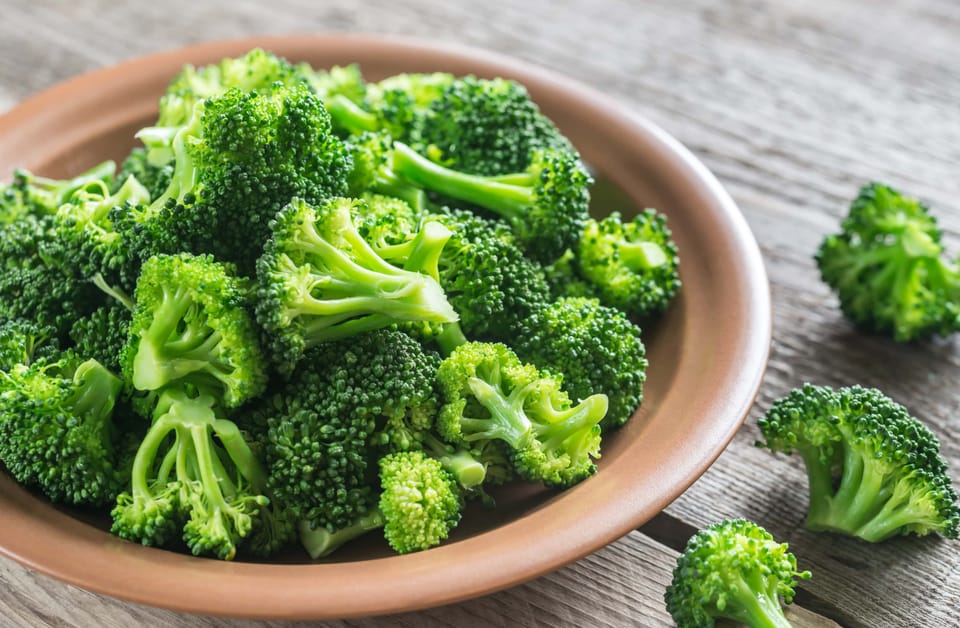
1. Broccoli

Broccoli was created by humans and is selectively grown from wild cabbage plants. It belongs to the genus Brassica oleracea, along with other cultivars, including Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and kale.
Ultimately, broccoli is a great source of vitamins C and K, fiber, antioxidants, and other minerals, making it a wholesome and tasty addition to any diet. A nutrient-dense vegetable like broccoli may benefit your wellness in an array of ways, including lowering inflammation, regulating blood sugar better, increasing immunity, and enhancing heart health.
2. Apple
Apples were developed from wild crabapples through selective breeding, and are available in numerous types of apples we love today. They are the product of countless generations of farmers and growers carefully breeding apple trees for desired features like sweetness, color, texture, and size.
Despite being artificial, this fruit is pleasant, delightful, and full of diverse antioxidants, fiber, and vitamin C. Research links apples to a relatively low risk of major serious illnesses, especially heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. Additionally, apples may aid in weight loss and improve the digestive tract and cognitive performance.
3. Banana

Banana is a fruit that prehistoric people created by selectively breeding wild bananas. This deliberate breeding yielded the Cavendish banana, which was developed for the first time in the late nineteenth century and is currently the most commonly recognized banana variation in the world.
Over time, this breed has subsequently grown to be the most common banana type worldwide. When it is regularly ingested, it can contribute to regulating heart rate and blood pressure. Bananas are a fruit that makes a tasty and beneficial treat and are a good source of fiber, vitamins B6 and C, and potassium. In addition, they contain fiber and antioxidants, which aids digestive and cardiovascular function.
4. Cauliflower

Cauliflower was selectively grown from wild cabbage plants originally by farmers in ancient Rome. Growers have been able to create many types of cauliflower by selective breeding that varies in size, color, flavor, and form. Cauliflower is a nutrient-rich vegetable high in vitamins C and K, and antioxidants, making it a useful and healthful addition to any diet. As a cruciferous vegetable, it naturally contains fiber and B vitamins.
Furthermore, its phytonutrients and antioxidant properties aid in preventing cancer. Additionally, it includes choline, which is crucial for memory and learning, fiber to aid in weight reduction, as well as many other vital nutrients.
5. Corn

Corn, commonly referred to as maize, is a man made vegetable developed by selective breeding from the teosinte wild grass. Teosinte has tiny, tough kernels limited in number on each cob, which is considerably different from modern corn. The teosinte plant, cultivated and selectively bred over several thousand years by ancient farmers in Central America, gradually evolved into the tall, fruitful maize plant that we are familiar with today. Early human cultures considered the discovery of maize a significant advance because it offered a consistent food supply they could maintain for a long time.
Due to its high fiber content and nutritional value, maize is a staple meal in many communities worldwide. Corn is a good source of the antioxidant, Vitamin C, which protects and defends your cells from harm and fends off illnesses, including cancer and heart disease. The carotenoids zeaxanthin and lutein, which are beneficial for eye health and aid in preventing cataract development, are abundant in yellow maize.
6. Strawberries

In Europe in the 18th century, an accidental hybridization of two wild strawberry species led to the development of the contemporary garden strawberry we consume today. The hybrid progeny was then selectively bred to produce the bigger, tastier, and more flavorful fruit we are familiar with today. Since then, gardeners have carefully bred strawberries to produce several types with various traits, including the fruit's size, shape, color, and flavor.
Vitamin C and other antioxidants in strawberries can lower the chance of developing major illnesses like diabetes, stroke, cancer, and heart disease. They are also a great source of potassium, folate, and phosphorus.
7. Eggplant
Eggplants, also known as the aubergine, originated in India or Southeast Asia, and farmers have developed bigger and sweeter kinds of eggplant throughout time through selective breeding. The numerous hues and forms of eggplants that we have now are due to selective breeding. Also, certain eggplant cultivars use selective breeding to produce fewer seeds, making the eggplant more palatable.
Antioxidants in eggplant, such as vitamins A and C, help shield cells from harm and strengthen immune function and cell regeneration. In addition, eggplant has a lot of polyphenols, which are organic plant molecules. If you have diabetes, these chemicals may improve how well your cells digest sugar. Moreover, they include complex B vitamins, including B5 and B6. B6 contributes to the manufacture of brain neurotransmitters, including serotonin, melatonin, and dopamine believed to aid in fear and anxiety management.
8. Tomatoes
Tomatoes, regarded as a man made fruit, were originally developed in South America, but were deliberately selected and grown to produce the bigger, sweeter, and juicier variety we enjoy presently. Until the 1800s, people rarely ate tomatoes since farmers thought them to be deadly. However, farmers were able to make tomatoes more appealing by selectively selecting them to have fewer harmful substances.
The succulent, flavorful, and antioxidant-rich tomatoes may help fend off a variety of health conditions. Lycopene, a plant chemical related to improved overall health, anticarcinogenic, and sunburn protection, is particularly abundant in them.
9. Watermelon

Watermelons have an unknown origin, although there is a high probability that their domestication started in Africa thousands of years ago. The bigger, sweeter, juicier types of watermelons we enjoy today were developed throughout time by humans via selective breeding and cultivation. Farmers have been able to produce watermelons with particular characteristics, such as thicker rinds, more sugar, and seedless types, by selective breeding. These characteristics have increased customers' desire for and attraction to watermelons. Citrulline is a prevalent organic compound in watermelon that may promote the circulation of blood and decrease high blood pressure.
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned about fruits that are man made and vegetables that are man made. Man made vegetables and fruits hybridized have more resistance and fare better in extremes of heat, drought, and cold. They provide stable, greater yields with maturation times that can easily be predicted, which is a great advantage. This way, farmers can now feed a more extensive world population while minimizing the effects of crop failure and pests. In addition, they carry diverse advantages including disease resistance, better yield, superior flavor, and longer shelf life. Other man made fruits and vegetables include oranges, peanuts, cranberries, and tangerines.






